In Ethernet networks, several devices work together to ensure smooth data transmission and connectivity. Among these devices, switches, hubs, and routers play crucial roles at different stages of the network. Despite their distinct functions, these devices are often integrated into a single unit, leading to confusion about their roles. This blog aims to demystify the distinctions between switch hub and routers, providing a clear understanding of their functionalities and how they contribute to network efficiency.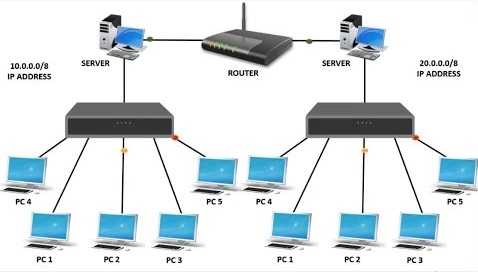
The Basics of Network Devices
To comprehend the differences between switches, hubs, and routers, it’s essential to grasp their basic definitions and functions:
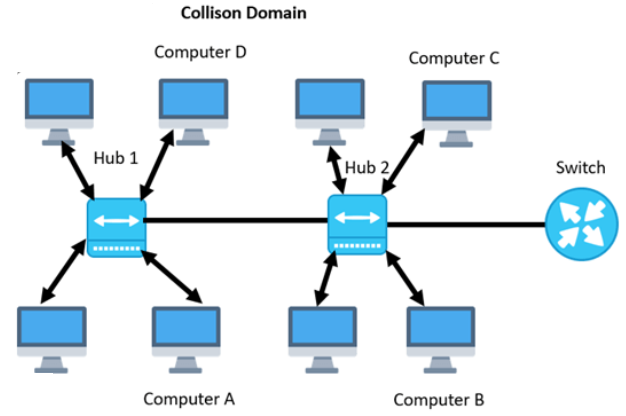
- Hub: A hub is a basic networking device that connects multiple Ethernet devices in a network. It operates at the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model and broadcasts incoming data packets to all connected devices, regardless of the intended recipient. This can lead to network inefficiencies and collisions, as all devices receive the data whether needed or not.
- Switch: A switch, on the other hand, is a more advanced device that operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. It connects multiple devices within a network and intelligently directs incoming data packets to the specific device based on MAC addresses. This targeted data transmission reduces collisions and enhances network efficiency.
- Router: A router operates specifically at the network layer, which is also known as Layer 3, of the OSI model. Its primary responsibility is to efficiently forward data packets between different networks. It uses IP addresses to determine the best path for data transmission, ensuring that packets reach their correct destination. Routers are essential for connecting different network segments and facilitating communication between devices on separate networks.

Hub vs. Switch vs. Router: Key Differences
To further clarify the distinctions between these network devices, let’s delve into their specific characteristics and functionalities:
Hub: Basic Connectivity
- Functionality: A hub serves as a simple connection point for multiple Ethernet devices. It broadcasts incoming data packets to all connected devices, leading to potential data collisions and network inefficiencies.
- Operation: Operates at the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model.
- Data Handling: This does not filter or manage data packets; all data is sent to all ports.
- Use Case: Suitable for small, simple networks where data traffic is minimal and advanced data management is not required.
Switch: Intelligent Data Management
- Functionality: A switch connects multiple devices within a network and directs incoming data packets to the appropriate device based on MAC addresses. This targeted approach minimizes collisions and optimizes network performance.
- Operation: Operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, and some advanced switches can also operate at the network layer (Layer 3).
- Data Handling: Filters and forwards data based on MAC addresses, ensuring efficient data transmission.
- Use Case: Ideal for larger networks with moderate to high data traffic, where efficient data management and collision reduction are essential.
Router: Inter-Network Communication
- Functionality: A router connects different networks and directs data packets between them using IP addresses. It determines the best path for data transmission, ensuring that packets reach their correct destination.
- Operation: Operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
- Data Handling: Routes data between networks based on IP addresses, facilitating communication between different network segments.
- Use Case: Essential for connecting different network segments, such as a local area network (LAN) to a wide area network (WAN), and for managing traffic between different network environments.
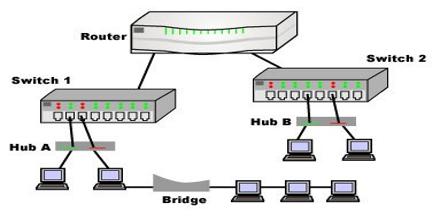
Integrated Devices: Combining Functions
Modern network devices often integrate the functionalities of hubs, switches, and routers into a single unit. This integration can simplify network management and reduce hardware costs. However, understanding the distinct roles of each component is crucial for optimizing network performance and addressing specific network needs.
For instance, a typical home or small office router often includes built-in switch and hub functionalities, providing both local device connectivity and inter-network communication. Despite this integration, the underlying principles of how data is managed and transmitted remain based on the distinct roles of switches, hubs, and routers.
Choosing the Right Device for Your Network
Selecting the appropriate network device depends on your specific network requirements and the scale of your operations:
- For Small, Simple Networks: A hub may suffice if you have a minimal number of devices and low data traffic. However, the lack of data filtering and the potential for collisions may hinder performance as your network grows.
- For Medium to Large Networks: A switch is a better choice for networks with moderate to high data traffic. Its ability to manage and direct data efficiently ensures optimal performance and minimizes collisions.
- For Connecting Multiple Networks: A router is essential for networks that require communication between different segments, such as connecting a LAN to the internet. Routers provide the necessary routing capabilities to ensure data reaches its intended destination across different networks.

Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between switch hub and routers is vital for designing and maintaining efficient network infrastructures. While these devices can be integrated into a single unit, their roles in data transmission and network management are distinct and critical. By comprehending the unique functionalities of each device, network administrators can make informed decisions that enhance network performance, reduce data collisions, and ensure seamless communication across different network segments. Whether for small home networks or large enterprise environments, choosing the right device is key to achieving optimal network efficiency and reliability.
This post was created with our nice and easy submission form. Create your post!